 Did you know that viruses, ransomware, spyware, and trojans are all categorized as types of malware? Having been around for decades, these cyber threats have grown both in number and intensity. Needless to say, it pays to know how each of them works as well as how to protect your business.
Did you know that viruses, ransomware, spyware, and trojans are all categorized as types of malware? Having been around for decades, these cyber threats have grown both in number and intensity. Needless to say, it pays to know how each of them works as well as how to protect your business.
Viruses
Once created to annoy users by making small changes to their computers, like altering wallpapers, this type of malware has evolved into a malicious tool used to breach confidential data. Most of the time, viruses work by attaching themselves to .exe files in order to infect computers once the file has been opened. This can result in various issues with your computer’s operating system, at their worst, rendering your computer unusable.
To avoid these unfortunate circumstances, you should scan executable files before running them. There are plenty of antivirus software options, but we recommend choosing one that scans in real-time rather than manually.
Spyware
Unlike viruses, spyware doesn’t harm your computer, but instead, targets you. Spyware attaches itself to executable files and once opened or downloaded, will install itself, often times completely unnoticed. Once running on your computer, it can track everything you type, including passwords and other confidential information. Hackers can then use this information to access your files, emails, bank accounts, or anything else you do on your computer.
But don’t panic just yet, you can protect yourself by installing anti-spyware software, sometimes included in all-purpose “anti-malware” software. Note that most reputable antivirus software also come bundled with anti-spyware solutions.
Adware
Are you redirected to a particular page every time you start your browser? Do you get pop ups when surfing the internet? If either situation sounds familiar, you’re likely dealing with adware. Also known as Potential Unwanted Programs (PUP), adware isn’t designed to steal your data, but to get you to click on fraudulent ads. Whether you click on the ad or not, adware can significantly slow down your computer since they take up valuable bandwidth. Worse still, they’re often attached with other types of malware.
Some adware programs come packaged with legitimate software and trick you into accepting their terms of use, which make them especially difficult to remove. To eradicate adware, you’ll need a solution with specialized adware removal protocols.
Scareware
This type of malware works like adware except that it doesn’t make money by tricking you into clicking on ads, but by scaring you into buying a software you don’t need. An example is a pop up ad that tells you your computer is infected with a virus and you need to buy a certain software to eliminate it. If you fall for one of these tactics and click on the ad, you’ll be redirected to a website where you can buy the fake antivirus software.
Scareware acts more like a diversion from the other malware that often comes with it. A good antivirus solution will help scan for scareware too, but you should patch your operating systems regularly just to be safe.
Ransomware
Ransomware has become increasingly common and hostile. It encrypts your computer files and holds them hostage until you’ve paid a fee for the decryption code. Because ransomware comes with sophisticated encryption, there aren’t many options unless you have backups of your data.
There are some tools that can protect against ransomware but we recommend that you backup your data and practice safe web browsing habits.
Worms
Similar to viruses, worms replicate themselves to widen the scope of their damage. However, worms don’t require human intervention to replicate themselves as they use security flaws to transmit from one computer to the next, making them far more dangerous than your typical virus. They often spread via email, sending emails to everyone in an infected user’s contact list, which was exactly the case with the ILOVEYOU worm that cost businesses approximately $5.5 billion worth of damage.
The easiest ways to protect your network from worms is to use a firewall to block external access to your computer network, and to be careful when clicking on unknown links in your email or unknown messages on social media.
Trojans
Usually downloaded from rogue websites, Trojans create digital backdoors that allow hackers to take control of your computer without your knowledge. They can steal your personal information, your files, or cause your computer to stop working. Sometimes hackers will use your computer as a proxy to conceal their identity or to send out spam.
To avoid trojan attacks, you should never open emails or download attachments from unknown senders. If you’re skeptical, use your antivirus software to scan every file first.
In order to keep malware at bay, you need to invest in security solutions with real-time protection and apply security best practices within your office. If you have any questions or concerns, or simply need advice on how to strengthen your business’s security, just give us a call and we’ll be happy to help.

 A new, Locky-type ransomware is currently infecting tens of thousands of computers worldwide. It uses the same code from the 2016 version to encrypt users’ files and it looks poised to cause another massive cyber emergency. Here’s everything we know so far.
A new, Locky-type ransomware is currently infecting tens of thousands of computers worldwide. It uses the same code from the 2016 version to encrypt users’ files and it looks poised to cause another massive cyber emergency. Here’s everything we know so far. Did you know that viruses, ransomware, spyware, and trojans are all categorized as types of malware? Having been around for decades, these cyber threats have grown both in number and intensity. Needless to say, it pays to know how each of them works as well as how to protect your business.
Did you know that viruses, ransomware, spyware, and trojans are all categorized as types of malware? Having been around for decades, these cyber threats have grown both in number and intensity. Needless to say, it pays to know how each of them works as well as how to protect your business.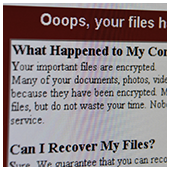 The cyber community hasn’t fully recovered from the WannaCry ransomware attacks, which struck businesses and organizations in May. Now, a Petya ransomware variant named Nyetya is poised to join its ranks as one of the worst cyber attacks in history. Like WannaCry, its attackers exploited unpatched Microsoft vulnerabilities and demanded a $300 ransom in Bitcoins. But there are key differences between the two that are worth taking a look.
The cyber community hasn’t fully recovered from the WannaCry ransomware attacks, which struck businesses and organizations in May. Now, a Petya ransomware variant named Nyetya is poised to join its ranks as one of the worst cyber attacks in history. Like WannaCry, its attackers exploited unpatched Microsoft vulnerabilities and demanded a $300 ransom in Bitcoins. But there are key differences between the two that are worth taking a look. WannaCry is one of the few malware campaigns to become a household name. It’s educated countless people on the reality of ransomware and the vulnerability of their data. If you’re still worried about whether you’re at risk, we’ve collected everything you need to know right here.
WannaCry is one of the few malware campaigns to become a household name. It’s educated countless people on the reality of ransomware and the vulnerability of their data. If you’re still worried about whether you’re at risk, we’ve collected everything you need to know right here. You pay close enough attention to the links you click to avoid clicking on something like goolge.com or evrenote.com…right? Because if you’re not, you could end up exposing your computer or smartphone to a host of malware. The newest phishing attack strategy is the worst of all, and can catch even the most astute users off guard.
You pay close enough attention to the links you click to avoid clicking on something like goolge.com or evrenote.com…right? Because if you’re not, you could end up exposing your computer or smartphone to a host of malware. The newest phishing attack strategy is the worst of all, and can catch even the most astute users off guard. It makes a lot of sense for electronics firms to pack a variety of functions into mobile devices and expand their usefulness. Instead of confining their use to communications, companies such as Apple, Samsung, and others have turned mobile phones into mini-computers that can serve as a substitute for your laptop, or as a storage device. If you’re using mobile phones as a communications and storage device, backing up now would be a wise move.
It makes a lot of sense for electronics firms to pack a variety of functions into mobile devices and expand their usefulness. Instead of confining their use to communications, companies such as Apple, Samsung, and others have turned mobile phones into mini-computers that can serve as a substitute for your laptop, or as a storage device. If you’re using mobile phones as a communications and storage device, backing up now would be a wise move. Although a ransomware infection might feel targeted, you’re not the only one who’s been infected. Ransomware is spreading at an alarming rate, but the further it goes, the more resources are allocated to fighting it. If your data is held hostage, always check these lists for free decryptors first.
Although a ransomware infection might feel targeted, you’re not the only one who’s been infected. Ransomware is spreading at an alarming rate, but the further it goes, the more resources are allocated to fighting it. If your data is held hostage, always check these lists for free decryptors first. Cybersecurity is one of the final bastions of hardware superiority. More and more IT solutions are being hosted in the cloud, and business owners are being told that software is all they need to get the job done, which is half true. When it comes to perimeter security you definitely need a hardware firewall, with a little something extra…
Cybersecurity is one of the final bastions of hardware superiority. More and more IT solutions are being hosted in the cloud, and business owners are being told that software is all they need to get the job done, which is half true. When it comes to perimeter security you definitely need a hardware firewall, with a little something extra…