 When you visit an encrypted website, the connection between the source of the web page and your browser is secure. Encryption ensures users’ browsing habits are safe from hackers’ prying eyes, but phishing scammers have found a way to adopt it for their own schemes.
When you visit an encrypted website, the connection between the source of the web page and your browser is secure. Encryption ensures users’ browsing habits are safe from hackers’ prying eyes, but phishing scammers have found a way to adopt it for their own schemes.
How hackers use encryption to carry out phishing scams
According to recent research, 24% of phishing scams in 2017 use web encryption — an astounding increase from last year’s 3%. This means more HTTPS sites may not be truly safe.
Phishing scammers rely on their victims to do what they ask, which is why it’s so effective. And with this new trick, unsuspecting users are more likely to be deceived. What makes this encryption-aided scam even more effective — and dangerous — is that it makes hackers’ phishing email or text that much more authentic-looking.
For example, if you receive an email that purports to be from Amazon and includes a link to an encrypted site, there’s now a slightly higher chance you’d believe this email is the real deal. Clearly, if you’ve never purchased anything from Amazon, you’d know that this is a fake. But then again, there are millions of Amazon customers who could be misled into thinking that that email is legitimate.
Does encryption mean a safer internet?
With organizations like the Internet Security Research Group and Google promoting encryption, the world wide web should be a safer place, but that’s not necessarily the case. In fact, encrypting more legitimate websites could simply result in an increased number of encrypted phishing sites.
It may also be useful to know that not all phishing sites use encryption. Many phishing scams are still carried out using websites that may or may not be encrypted.
What you can do to ensure safety
This isn’t meant to cause panic, and despite this new phishing tactic, encryption is still an essential security tool that every business must implement.
Websites with HTTPS are still much safer than unencrypted ones. This is why it’s more important than ever to be vigilant when visiting suspicious sites and clicking on links. If you receive an email from PayPal asking you to verify your bank account details or password to a seemingly secure link, be wary. Some phishing scams are easy to detect, but some are not.
Practice extreme caution when responding to requests for sensitive data. Consider the source of the message, think before clicking, and don’t hesitate to seek the advice of an expert in case you have doubts. Phishers succeed only if you do what they ask you to do.
Phishing and other cyber scams are constantly getting upgrades, and no single solution can prevent hackers from attacking you. But your business could be much safer with the right cyber security protections in place. If this is exactly what you need, get in touch with our cyber security technicians.

 You might be entering credit card details on a website to purchase something online or filling in your personal information to subscribe to a service, thinking you’re safe behind the keyboard. And you probably are — if the computer you’re using doesn’t have a keylogger installed. But for HP laptop users, chances are they aren’t so lucky. Read on to see why.
You might be entering credit card details on a website to purchase something online or filling in your personal information to subscribe to a service, thinking you’re safe behind the keyboard. And you probably are — if the computer you’re using doesn’t have a keylogger installed. But for HP laptop users, chances are they aren’t so lucky. Read on to see why. Did you know that viruses, ransomware, spyware, and trojans are all categorized as types of malware? Having been around for decades, these cyber threats have grown both in number and intensity. Needless to say, it pays to know how each of them works as well as how to protect your business.
Did you know that viruses, ransomware, spyware, and trojans are all categorized as types of malware? Having been around for decades, these cyber threats have grown both in number and intensity. Needless to say, it pays to know how each of them works as well as how to protect your business.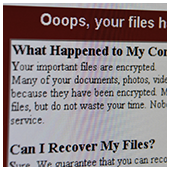 The cyber community hasn’t fully recovered from the WannaCry ransomware attacks, which struck businesses and organizations in May. Now, a Petya ransomware variant named Nyetya is poised to join its ranks as one of the worst cyber attacks in history. Like WannaCry, its attackers exploited unpatched Microsoft vulnerabilities and demanded a $300 ransom in Bitcoins. But there are key differences between the two that are worth taking a look.
The cyber community hasn’t fully recovered from the WannaCry ransomware attacks, which struck businesses and organizations in May. Now, a Petya ransomware variant named Nyetya is poised to join its ranks as one of the worst cyber attacks in history. Like WannaCry, its attackers exploited unpatched Microsoft vulnerabilities and demanded a $300 ransom in Bitcoins. But there are key differences between the two that are worth taking a look.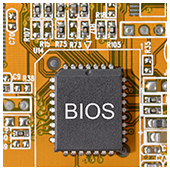 As workplace IT gets more and more hi-tech, the average user gets further from the building blocks that keep it running. At times that seems like a good thing, but if you aren’t aware of the most basic aspects of your hardware, you could be vulnerable to a nasty cyber attack. Make sure you’re secure with the help of our firmware advice.
As workplace IT gets more and more hi-tech, the average user gets further from the building blocks that keep it running. At times that seems like a good thing, but if you aren’t aware of the most basic aspects of your hardware, you could be vulnerable to a nasty cyber attack. Make sure you’re secure with the help of our firmware advice. Do you have security measures in place for your office’s printers? By “security,” we don’t mean locked doors or watchful guards; we’re referring to security against hackers that use printers as a weapon. Despite many companies going paperless, printers are still essential in most offices. And based on recent reports, popular printer brands are targeted for corruption.
Do you have security measures in place for your office’s printers? By “security,” we don’t mean locked doors or watchful guards; we’re referring to security against hackers that use printers as a weapon. Despite many companies going paperless, printers are still essential in most offices. And based on recent reports, popular printer brands are targeted for corruption. Ransomware has become a fast-track for making money for some hackers this holiday season. But instead of just demanding a small payment for the decryption code that will unlock their computers, some hackers are demanding that victims sacrifice two other friends to ensure they receive the code they need. Read more to find out what makes Popcorn Time such a devious program and how you can avoid becoming one of its victims.
Ransomware has become a fast-track for making money for some hackers this holiday season. But instead of just demanding a small payment for the decryption code that will unlock their computers, some hackers are demanding that victims sacrifice two other friends to ensure they receive the code they need. Read more to find out what makes Popcorn Time such a devious program and how you can avoid becoming one of its victims. As shown by recent high-profile hacking scandals – targeting everyone from Sony Entertainment to the extramarital-affair-facilitating website Ashley Madison – cyber crime shows no sign of disappearing any time soon. In fact, experts predict that 2016 is going to be an even busier year for cyber criminals, hackers and scammers. So what do you need to know in order to be able to keep your small or medium-sized business safe next year? Here we take a look at what could be in store.
As shown by recent high-profile hacking scandals – targeting everyone from Sony Entertainment to the extramarital-affair-facilitating website Ashley Madison – cyber crime shows no sign of disappearing any time soon. In fact, experts predict that 2016 is going to be an even busier year for cyber criminals, hackers and scammers. So what do you need to know in order to be able to keep your small or medium-sized business safe next year? Here we take a look at what could be in store.